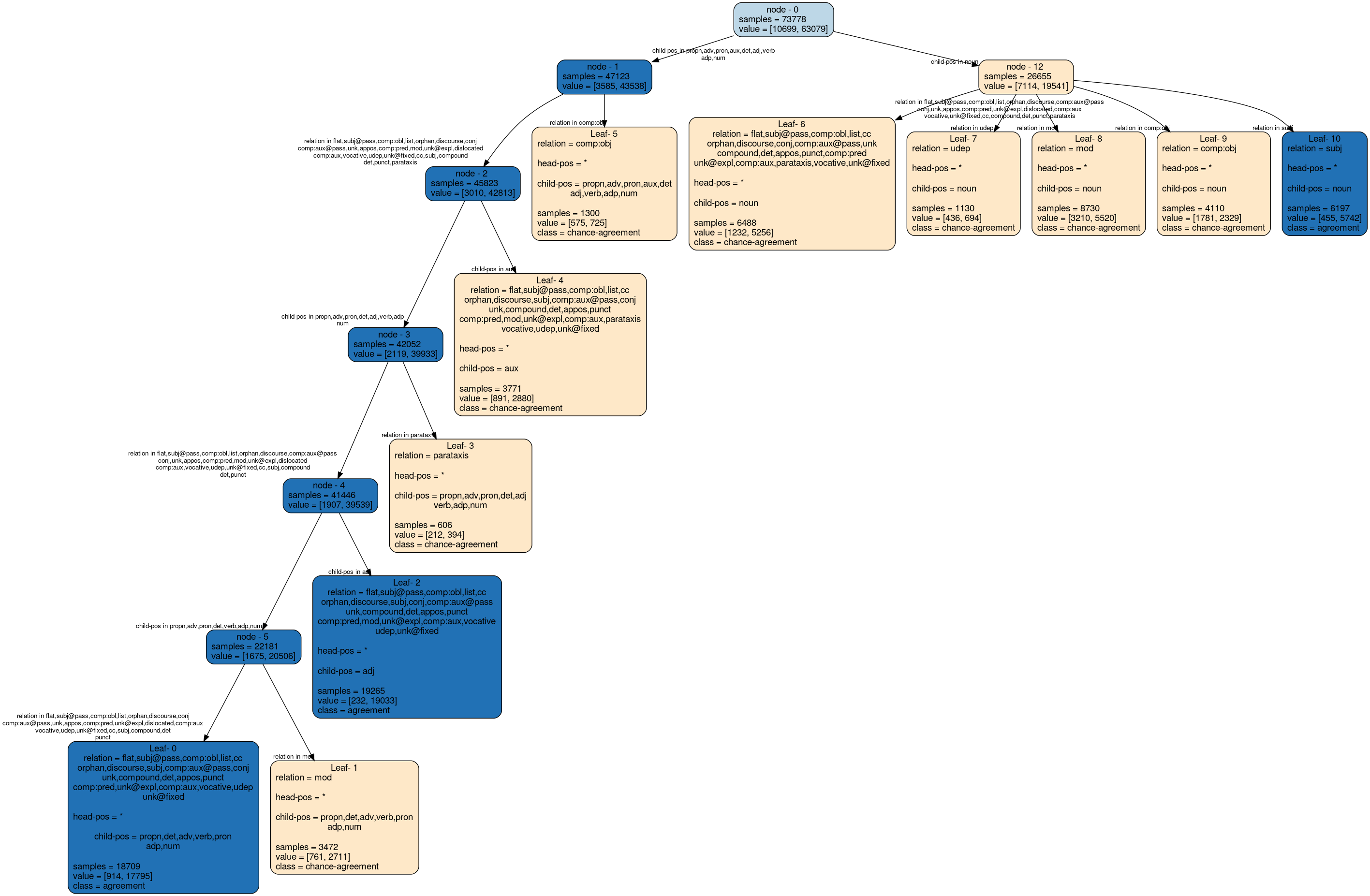
Token Distribution across Number
The following histogram captures the token distribution per different part-of-speech (POS) tags.
Legend on the top-right shows the different values the Number attribute takes.
'NA' denotes those tokens which do not possess the Number attribute.
Token examples for each POS:
Number agreement rules:
The following decision tree visualizes the rules used for classifying presence/absence of morphological agreement between two tokens that are connected by a dependency relation denoted by relation. head-pos and child-pos refer to the POS tag of the head and child token respectively.
Each node of the tree represents a portion of the data. samples denotes the number of training data points in that node. value is the class distribution within that node. Each edge denotes the feature used for splitting.
Leaf nodes contain the description of all of the features that appear in that leaf. * denotes that the feature can take any value.
Tree for p=0.01
Click on to show summary of agreement rules.
- ADJ tokens agree with their head for the dependency relations: orphan(orphan), modifer(mod), complement for auxiliary(comp:aux@pass), compound(compound), predicative complements(comp:pred), punctuation(punct)
- NOUN tokens agree with their head for the dependency relations: subject(subj)
- VERB tokens agree with their head for the dependency relations: complement for auxiliary(comp:aux), unk(unk)
- DET tokens agree with their head for the dependency relations: determiner(det), underspecified dependency(udep), unk@fixed(unk@fixed), unk@expl(unk@expl), discourse element(discourse)
- All tokens agree with their head tokens for the dependency relations: conjunct (conj), coordinating conjunction (cc)
- PROPN tokens agree with their head for the dependency relations: flat multiword expression(flat), appositional modifier(appos), list(list), subject(subj@pass), vocative(vocative)
- PRON tokens agree with their head for the dependency relations: oblique complements(comp:obl)
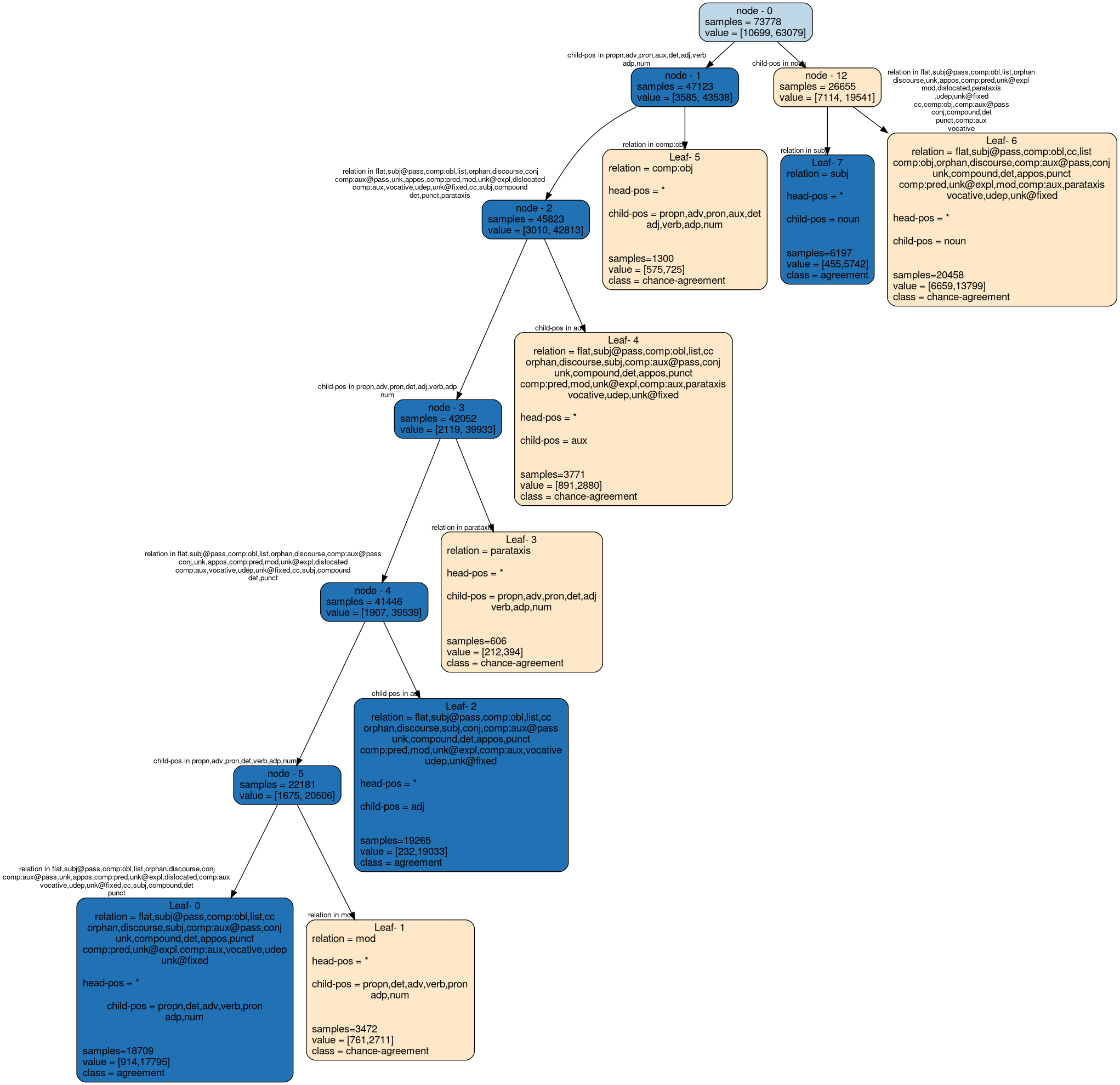
Examples for each leaf node:
Click on to expand the tree.